מדוע תרופות נוגדות דיכאון כגון ציפרלקס עשויות לגרום לבעיות בתפקוד המיני ומהן אפשרויות הטיפול לאילו החווים תופעות לוואי מסוג זה
ירידה בחשק המיני ובעיות בתפקוד המיני יכולים מצד אחד להוות סימפטומים של דיכאון, אך מצד שני סימפטומים אלו גם יכולים להיות חלק מתופעות הלוואי של תרופות נוגדות דיכאון.
ההגדרה של תופעת לוואי מינית כוללת בתוכה תופעות לוואי תרופתיות הפוגעות ביכולת לקיים יחסי מין. הן יכולות לבוא לידי ביטוי עוד בשלב שלפני תחילת יחסי המין (כשיש ירידה בחשק המיני), בשלב הראשוני של יחסי המין (כמו הפרעות זקפה) או במהלך קיום יחסי המין (כאשר יש קושי להגיע לאורגזמה).
למעשה, תרופות נוגדות דיכאון הן מבין קבוצות התרופות שהכי מזוהות עם בעיות בתפקוד המיני בגברים, ובראשן משפחת תרופות ה- SSRIs (מעכבי ספיגה חוזרת של סרוטונין) אליה משתייכת התרופה הפופולרית ציפרלקס שגורמת לתופעות לוואי מיניות בכ- 60% מהמטופלים שנוטלים אותן באופן קבוע. תופעות הלוואי המיניות הנפוצות של ציפרלקס בקרב גברים הן ירידה בחשק המיני, קושי להגיע לאורגזמה וקושי להשיג או לשמר זקפה. אמנם תרופות נוגדות דיכאון מהוות בדרך כלל חלק בלתי נפרד מהטיפול במחלה, אך מכיוון שהמיניות מהווה חלק חשוב מאוד מהחיים הבריאים, תופעות לוואי מיניות כתוצאה מהטיפול בנוגדי דיכאון עלולות להיות מתסכלות למדי.
כיצד ציפרלקס גורמת להפרעות זקפה?
כאמור, ציפרלקס משתייכת למשפחה של תרופות הנקראת מעכבי ספיגה חוזרת של סרוטונין (SSRIs). היא מטפלת בדיכאון וחרדה על ידי העלאת הרמות של המתווך העצבי סרוטונין שתורם לתחושת שלווה, רוגע וליציבות מצב הרוח. למרות שהקשר בין עלייה ברמות הסרוטונין והפרעות זקפה עדיין לא הוברר במלואו, ישנן מספר תיאוריות מדעיות שמנסות להסביר זאת. אחת התיאוריות קשורה לכך שהרמות הגבוהות של המוליך העצבי סרוטונין מובילות לירידה ברמות של דופמין – המוליך העצבי הקשור לחוויית העונג . מכאן, רמות נמוכות של דופמין עלולות להתבטא בקושי להגיע לעוררות מינית כמו גם בקושי לשמר ולחוות עונג מיני ברמה עוצמתית יותר. כמו כן, ידוע כי תרופות ממשפחת ה- SSRIs מקושרות לירידה במספר הזקפות הליליות שגברים חווים במהלך השינה ועם היעדר זקפת בוקר1, ועובדה זו עשויה אף היא להיות קשורה לעלייה ברמת הסרוטונין ולפגיעה בשנת החלום החיונית להתרחשות של זקפה במהלך הלילה ועם היקיצה.
מעבר לכך, ידוע כי תרופות ממשפחת ה- SSRIs עשויות לגרום לעלייה ברמת ההורמון פרולקטין שעלולה להתבטא בקושי להגיע לאורגזמה. מחקרים במודלים של בע”ח אף הצביעו על קשר בין תרופות אלו לירידה ברמות ההורמון הגברי טסטוסטרון, מה שעשוי להיות קשור לירידה בחשק המיני.
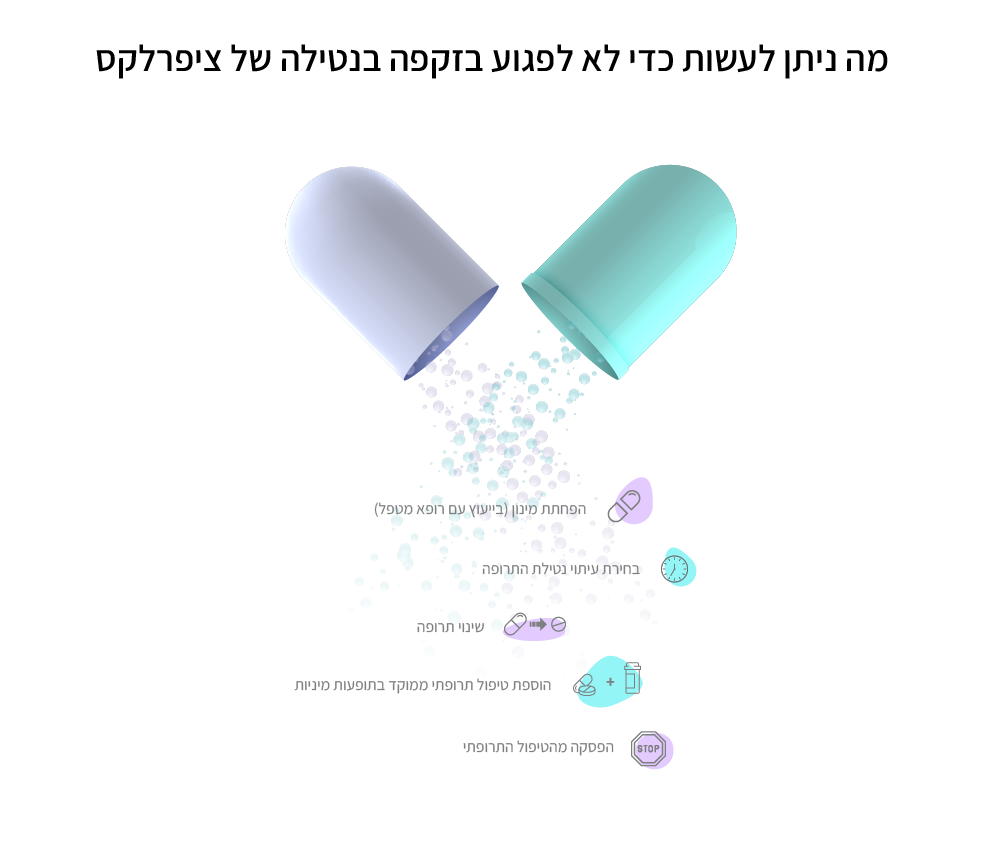
מה ניתן לעשות כשחווים הפרעות זקפה ותופעות לוואי מיניות?
ישנן מספר גישות שניתן לאמץ בהתייעצות עם הרופא המטפל. לא תמיד הן יתאימו לכולם ולעיתים יש לאמץ יותר מפתרון מוצע אחד עד השגת שיפור בסימפטומים:
- הפחתת מינון – בתיאום עם הרופא המטפל ניתן במקרים מסוימים לנסות ולהפחית את מינון התרופה נוגדת הדיכאון. אצל חלק מהמטופלים די בהפחתת המינון כדי להביא לשיפור בתופעות הלוואי המיניות מבלי לפגוע ביעילות הטיפול במחלה. במחקרים שנעשו על פרוזק, מהתרופות האנטי-דכאוניות הראשונות, , נמצא כי הורדת המינון היומי מ- 20 מ”ג ל- 5-10 מ”ג תרמה להפחתה משמעותית בתופעות הלוואי תוך שמירה על ההשפעה נוגדת הדיכאון של התרופה.
- תזמון (טיימינג) – “תזמון זה הכל”, בפרט כשמדובר ביחסי מין. לכן אם לוקחים את התרופה רק פעם ביום, ניתן לנסות ליטול אותה לאחר קיום יחסי המין ולא לפני. למשל, אם אתה נוהג לקיים יחסי מין בדרך כלל בערב, תוכל לנסות לקחת את התרופה בשעות הבוקר. שיטה זו אולי לא תתאים לכולם, אך במידה וכן, החיסרון הוא הפגיעה בספונטניות של יחסי המין.
- שינוי התרופה – סוגים שונים של תרופות נוגדות דיכאון עשויים לגרום לפחות תופעות לוואי. למשל, ידוע כי תרופות שמערבות מנגנון פעולה שונה מתרופות ממשפחת ה- SSRIs גורמות לפחות תופעות לוואי מיניות, ובהתייעצות עם הרופא המטפל ניתן להחליף לתרופה נוגדת דיכאון אחרת. גישה נוספת היא הוספת תרופה נלווית לטיפול, כמו למשל הוספת התרופה נוגדת הדיכאון וולבוטרין לטיפול בתרופה ממשפחת ה- SSRIs במטרה למתן את תופעות הלוואי המיניות שלה.
- טיפול תרופתי ממוקד בתופעות הלוואי המיניות – הוספת תרופה ממשפחת התרופות לטיפול בהפרעות זקפה לטיפול התרופתי בדיכאון יכולה לתרום לשיפור התפקוד המיני של הגבר, כפי שעולה ממחקרים. כמו כן, הוספת טיפול על בסיס ג’ל טסטוסטרון יכול לשפר מצב של הפרעות זקפה בקרב גברים עם מחסור בטסטוסטרון המטופלים בתרופות נוגדות דיכאון ממשפחת ה- SSRIs.
- “חופשה” מהטיפול התרופתי – אצל חלק מהאנשים הפסקה של יום-יומיים בטיפול בתרופות נוגדות הדיכאון יכול לתרום להקלה על תופעות הלוואי המיניות, וזאת מבלי לפגוע ביעילות הטיפול. אולם חשוב לציין כי גישה זו לא מתאימה ליישום עם כל תרופה נוגדת דיכאון וחשוב להתייעץ על כך עם הרופא המטפל. כשלתרופה זמן מחצית חיים ארוך (כלומר התרופה נשארת בגוף לאורך זמן גם כשמפסיקים לקחת אותה), יותר בעייתי ליישם הפסקה יזומה שכזו.
[1] https://cdn.mdedge.com/files/s3fs-public/Document/September-2017/0912CP_Article1.pdf↩
החברה מבהירה בזאת כי המידע הכלול באתר הינו למטרות מידע בלבד, ואינו נועד להוות תחליף לייעוץ רפואי ובריאותי מקצועי ואינו מהווה ייעוץ או חוות דעת רפואית. פנה תמיד לייעוץ אצל הרופא שלך או גורם מוסמך אחר בכל מצב רפואי או שאלה שיש לך לגבי מצבך הרפואי.





